You and I and most other animals and plants are made up of billions of tiny cells. The term cell was first introduced by Robert Hooke, an English botanist, in 1665. Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell It was explained by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden in the year 1830.
Do you know what living things are made up of? How do they work and function accordingly? How do they look like their ancestors? It’s all cells! No, not those cells with batteries. These are human cells.
Cytology is a branch of biology. It explains the study of cells. Cytology differentiates cells in terms of physiological properties, their structure, the organelles they contain, interactions with their environment, their cycle, division, death, and cell function. Microscopic and molecular technique use to study cells.
What is a cell?
Like every building is made up of blocks similarly, cells are the building blocks of all living things. Prokaryotic. The most straightforward unit that can live independently is a cell. A human body has trillions of cells in it, between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. These cells are specialized in their nature of work. They take food from your body, create energy and carry their tasks. Hence, they provide structure for the body. Apart from their daily tasks, they also inhibit genetic information and make copies out of them.
For example, cells inside your bones make an exceptional substance called hemoglobin. This is the substance that makes your blood red. These cells in the bone marrow make hemoglobin by combining iron with an organic molecule. However, they don’t use the hemoglobin themself. They pack it and send it to red blood cells so they can carry it around your body.
What is the structure of a normal cell?
A cell is a unit of life. It consists of a mass of living matter protoplasm.
Protoplasm is a complex jelly-like substance in which endless chemical reactions are taking place. This is the living essence of a cell. It includes the cell surface membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. It exists in the sol (liquid) state and gel (semi-solid) state.
Nucleus:
The nucleus consists of a small spherical mass of denser protoplasm, the nucleoplasm. It is surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope. It is embedded within the cytoplasm of a cell. The nucleus is responsible for cell reproduction. It is vital to keep a cell alive and repairs worn-out parts.
Cytoplasm:
The part of the protoplasm surrounding the nucleus is known as the cytoplasm. It is where most life processes occur. The different important organelle is embedded within the cytoplasm. For example, mitochondria. Between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Aspherical or rod-shaped organelle. It is responsible for releasing energy from food substances during respiration.
Cell surface membrane:
Cell surface membrane or plasma membrane is a partially permeable membrane. It surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell.
It was vital to know about the basic structure of a cell. So, we can know more about prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells.
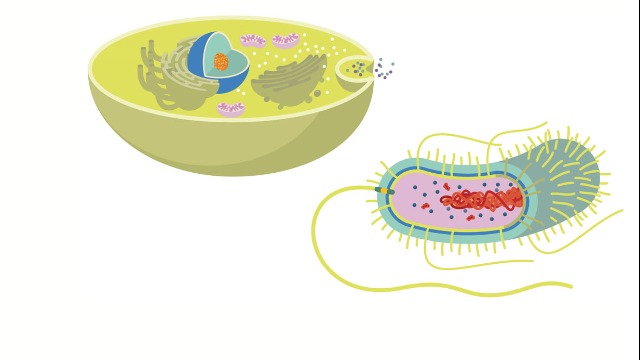
What is a prokaryotic cell? between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
A prokaryotic cell is derived from a prokaryote, which is a Greek word. It means pro karyon before nuclei in English. These are the oldest type of living organisms that ever existed in this world. Scientists found fossils dated back to 3.5 billion years ago. According to research, these cells came into life by gaining energy from the sun and chemical energy from the earth.
Scientists believe that these cells reproduced, keep changing, and adapting to new environments. Some believed that eukaryotes are raised through prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells are smaller in size compared to eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are elementary. They do not even possess a nucleus. They reproduce through the process of binary fission. A capsule envelopes prokaryotic cells as protection. The cell is hard and stiff in structure due to the presence of a cell wall in it. The cell wall is right under the enveloped capsule.
What is a eukaryotic cell? between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
The word eukaryotes came from the Greek word Eu Karyon which means suitable nuclei. These cells are very complex compared to prokaryotes. They are also more extensive. They include all the kingdoms.
The plasma membrane of the cell is guarded by a cell wall. The cell wall controls which substances must exit or enter the cell. The genetic information is stored in the nucleus, which is surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Synthesis of protein occurs in the nucleolus in the nucleus. The energy given to the cell produced by mitochondria in the nucleus.
Photosynthesis occurs in subcellular sites known as chloroplasts. These are present in only plant cells. Both animal and plant cells are eukaryotic with unique features. Both animal and plant cells are nearly similar. They have a nucleus, plasma membrane, and selectively permeable membrane. Both cells contain membrane-bound organelles with their defined functions. They have vacuoles. Vacuoles serve the purpose of storage and
keep the shape of the cell rigid. Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell. It stores and provides energy for any cellular activity.
A eukaryotic cell divides by the process of mitosis. It undergoes various stages during cell division. Those are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis.
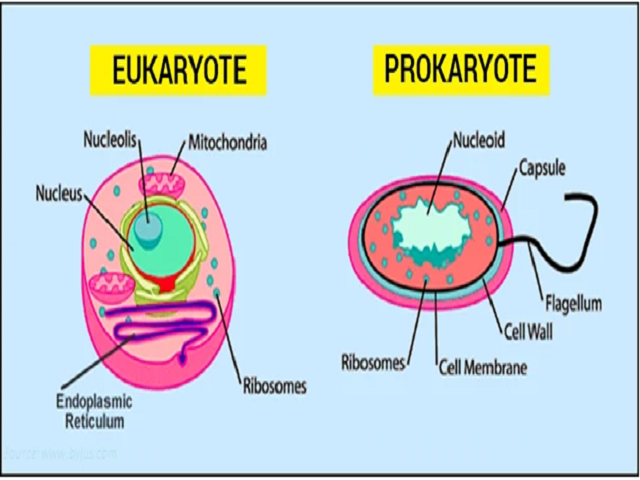
Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Let’s look at their differences side by side and how they are different from each other.
Type of cell
Prokaryotic cells: These are unicellular.
Eukaryotic cells: These are unicellular and multicellular.
Cell size: between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells: It has a diameter of 0.2 μm – 2.0 μm.
Eukaryotic cells: it has a diameter of 10 μm – 100 μm.
Cell wall: between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells: As its chemically complex, but most of the time, the cell wall is present.
Eukaryotic cells: It is chemically simple when the cell wall exists.
Nucleus
Prokaryotic cells: There is no nucleus.
Eukaryotic cells: It is present in these cells and more prominent than a normal nucleus.
Ribosomes
Prokaryotic cells: Yes, they are present in smaller sizes and spherical.
Eukaryotic cells: Yes, they are present in a comparatively larger size. They are linear in shape.
DNA arrangement
Prokaryotic cells: They exist in a circular arrangement.
Eukaryotic cells: They exist in a linear arrangement.
Mitochondria
Prokaryotic cells: It is absent here.
Eukaryotic cells: It is present here.
Cytoplasm
Prokaryotic cells: Cytoplasm is present in these cells, but there is no organelle in it.
Eukaryotic cells: Cytoplasm and organelles are present in these cells.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Prokaryotic cells: It is absent here.
Eukaryotic cells: It is present here.
Plasmids
Prokaryotic cells: It’s present in these cells.
Eukaryotic cells: It rarely found in these cells.
Ribosomes
Prokaryotic cells: They have small ribosomes.
Eukaryotic cells: They have large ribosomes.
Lysosomes: between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells: There are no lysosomes or centrosomes in these cells.
Eukaryotic cells: Both lysosomes and centrosomes are present here.
Cell division
Prokaryotic cells: It occurs through binary fission.
Eukaryotic cells: It occurs through mitosis.
Flagella: between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells: The small in size compared to the ones in eukaryotes.
Eukaryotic cells: They are comparatively larger than prokaryotes.
Reproduction: between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells: Asexual reproduction occurs here.
Eukaryotic cells: Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur here.
Examples
Prokaryotic cells: They include bacteria archaea.
Eukaryotic cells: They include plant and animal cells.
Therefore, we can say that cells divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes based on genetic materials enclosed by a nuclear envelope between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes don’t have membrane-bound organelles. On the contrary, eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles.
Also read: How many calories are in a cup of tea.








I know this web page gives quality depending articles and additional
stuff, is there any other site which provides these stuff in quality?ラブドール